It is easy to deploy servers to the cloud within a few minutes, you can have a cloud-based server that you (or others can use). ubuntu has a great guide on setting up basic security issues but what do you need to do.
If you do not secure your server expects it to be hacked into. Below are tips on securing your cloud server.
First, read more on scanning your server with Lynis security scan.
Always use up to date software
Always use update software, malicious users can detect what software you use with sites like shodan.io (or use port scan tools) and then look for weaknesses from well-published lists (e.g WordPress, Windows, MySQL, node, LifeRay, Oracle etc). People can even use Google to search for login pages or sites with passwords in HTML (yes that simple). Once a system is identified by a malicious user they can send automated bots to break into your site (trying millions of passwords a day) or use tools to bypass existing defences (Security researcher Troy Hunt found out it’s child’s play).
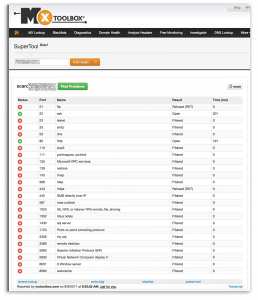
Portscan sites like https://mxtoolbox.com/SuperTool.aspx?action=scan are good for knowing what you have exposed.
You can also use local programs like nmap to view open ports
Instal nmap
Find open ports
Limit ssh connections
Read more here.
Use ufw to set limits on login attempts
Only allow known IP’s access to your valuable ports
sudo ufw allow from 123.123.123.123/32 to any port 22
Delete unwanted firewall rules
Only allow known IP’s to certain ports
Also, set outgoing traffic to known active servers and ports
Don’t use weak/common Diffie-Hellman key for SSL certificates, more information here.
More info on generating SSL certs here and setting here and setting up Public Key Pinning here.
Intrusion Prevention Software
Do run fail2ban: Guide here https://www.linode.com/docs/security/using-fail2ban-for-security
I use iThemes Security to secure my WordPress and block repeat failed logins from certain IP addresses.
iThemes Security can even lock down your WordPress.
You can set iThemes to auto lock out users on x failed logins
Remember to use allowed whitelists though (it is so easy to lock yourself out of servers).
Passwords
Do have strong passwords and change the root password provided by the hosts. https://howsecureismypassword.net/ is a good site to see how strong your password is from brute force password attempts. https://www.grc.com/passwords.htm is a good site to obtain a strong password. Do follow Troy Hunt’s blog and twitter account to keep up to date with security issues.
Configure a Firewall Basics
You should install a firewall on your Ubuntu and configure it and also configure a firewall with your hosts (e.g AWS, Vultr, Digital Ocean).
Configure a Firewall on AWS
My AWS server setup guide here. AWS allow you to configure the firewall here in the Amazon Console.
| Type | Protocol | Port Range | Source | Comment |
| HTTP | TCP | 80 | 0.0.0.0/0 | Opens a web server port for later |
| All ICMP | ALL | N/A | 0.0.0.0/0 | Allows you to ping |
| All traffic | ALL | All | 0.0.0.0/0 | Not advisable long term but OK for testing today. |
| SSH | TCP | 22 | 0.0.0.0/0 | Not advisable, try and limit this to known IP’s only. |
| HTTPS | TCP | 443 | 0.0.0.0/0 | Opens a secure web server port for later |
Configure a Firewall on Digital Ocean
Configuring a firewall on Digital Ocean (create a $5/m server here). You can configure your Digital Ocean droplet firewall by clicking Droplet, Networking then Manage Firewall after logging into Digital Ocean.
Configure a Firewall on Vultr
Configuring a firewall on Vultr (create a $2.5/m server here).
Don’t forget to set IP rules for IPV4 and IPV6, Only set the post you need to allow and ensure applications have strong passwords.
Ubuntu has a firewall built in (documentation).
Enable the firewall
Adding common ports
sudo ufw allow ssh/tcp sudo ufw logging on sudo ufw allow 22 sudo ufw allow 80 sudo ufw allow 53 sudo ufw allow 443 sudo ufw allow 873 sudo ufw enable sudo ufw status sudo ufw allow http sudo ufw allow https
Add a whitelist for your IP (use http://icanhazip.com/ to get your IP) to ensure you won’t get kicked out of your server.
sudo ufw allow from 123.123.123.123/24 to any port 22
More help here. Here is a good guide on ufw commands. Info on port numbers here.
If you don’t have a Digital Ocean server for $5 a month click here and if a $2.5 a month Vultr server here.
Backups
rsync is a good way to copy files to another server or use Bacula
Basics
Initial server setup guide (Digital Ocean).
Sudo (admin user)
Read this guide on the Linux sudo command (the equivalent if run as administrator on Windows).
Users
List users on an Ubuntu OS (or compgen -u)
Common output
Add User
e.g
Add user to a group
Show users in a group
This will show users in a group
Remove a user
Rename user
Change user password
Groups
Show all groups
compgen -ugCommon output
compgen -g root daemon bin sys adm tty disk lp mail proxy sudo www-data backup irc etc
You can create your own groups but first, you must be aware of group ids
cat /etc/group
Then you can see your systems groups and ids.
Create a group
Permissions
Read this https://help.ubuntu.com/community/FilePermissions
How to list users on Ubuntu.
Read more on setting permissions here.
Chmod help can be found here.
Install Fail2Ban
I used this guide on installing Fail2Ban.
Check Fail2Ban often and add blocks to the firewall of known bad IPs
Best practices
Ubuntu has a guide on basic security setup here.
Startup Processes
It is a good idea to review startup processes from time to time.
Accounts
- Read up on the concept of least privilege access for apps and services here.
- Read up on chmod permissions.
Updates
Do update your operating system often.
Minimal software
Only install what software you need
Exploits and Keeping up to date
Do keep up to date with exploits and vulnerabilities
- Follow 0xDUDE on twitter.
- Read the GDI.Foundation page.
- Visit the Exploit Database
- Vulnerability & Exploit Database
- Subscribe to the Security Now podcast.
Secure your applications
- NodeJS: Enable logging in applications you install or develop.
Ban repeat Login attempts with FailBan
Fail2Ban config
Hosts File Hardening
Add
Add a whitelist with your ip on /etc/fail2ban/jail.conf (see this)
Restart the service
sudo service fail2ban restart sudo service fail2ban status
Intrusion detection (logging) systems
Tripwire will not block or prevent intrusions but it will log and give you a heads up with risks and things of concern
Install Tripwire.
Running Tripwire
This will scan your system for issues of note
My Output.
sudo nano /var/log/tiger/security.report.username.170809-18:42
Security scripts *** 3.2.3, 2008.09.10.09.30 ***
Wed Aug 9 18:42:24 AEST 2017
20:42> Beginning security report for username (x86_64 Linux 4.4.0-89-generic).
# Performing check of passwd files...
# Checking entries from /etc/passwd.
--WARN-- [pass014w] Login (bob) is disabled, but has a valid shell.
--WARN-- [pass014w] Login (root) is disabled, but has a valid shell.
--WARN-- [pass015w] Login ID sync does not have a valid shell (/bin/sync).
--WARN-- [pass012w] Home directory /nonexistent exists multiple times (3) in
/etc/passwd.
--WARN-- [pass012w] Home directory /run/systemd exists multiple times (2) in
/etc/passwd.
--WARN-- [pass006w] Integrity of password files questionable (/usr/sbin/pwck
-r).
# Performing check of group files...
# Performing check of user accounts...
# Checking accounts from /etc/passwd.
--WARN-- [acc021w] Login ID dnsmasq appears to be a dormant account.
--WARN-- [acc022w] Login ID nobody home directory (/nonexistent) is not
accessible.
# Performing check of /etc/hosts.equiv and .rhosts files...
# Checking accounts from /etc/passwd...
# Performing check of .netrc files...
# Checking accounts from /etc/passwd...
# Performing common access checks for root (in /etc/default/login, /securetty, and /etc/ttytab...
--WARN-- [root001w] Remote root login allowed in /etc/ssh/sshd_config
# Performing check of PATH components...
--WARN-- [path009w] /etc/profile does not export an initial setting for PATH.
# Only checking user 'root'
# Performing check of anonymous FTP...
# Performing checks of mail aliases...
# Checking aliases from /etc/aliases.
# Performing check of `cron' entries...
--WARN-- [cron005w] Use of cron is not restricted
# Performing check of 'services' ...
# Checking services from /etc/services.
--WARN-- [inet003w] The port for service ssmtp is also assigned to service
urd.
--WARN-- [inet003w] The port for service pipe-server is also assigned to
service search.
# Performing NFS exports check...
# Performing check of system file permissions...
--ALERT-- [perm023a] /bin/su is setuid to `root'.
--ALERT-- [perm023a] /usr/bin/at is setuid to `daemon'.
--ALERT-- [perm024a] /usr/bin/at is setgid to `daemon'.
--WARN-- [perm001w] The owner of /usr/bin/at should be root (owned by daemon).
--WARN-- [perm002w] The group owner of /usr/bin/at should be root.
--ALERT-- [perm023a] /usr/bin/passwd is setuid to `root'.
--ALERT-- [perm024a] /usr/bin/wall is setgid to `tty'.
# Checking for known intrusion signs...
# Testing for promiscuous interfaces with /bin/ip
# Testing for backdoors in inetd.conf
# Performing check of files in system mail spool...
# Performing check for rookits...
# Running chkrootkit (/usr/sbin/chkrootkit) to perform further checks...
--WARN-- [rootkit004w] Chkrootkit has detected a possible rootkit installation
Possible Linux/Ebury - Operation Windigo installetd
# Performing system specific checks...
# Performing checks for Linux/4...
# Checking boot loader file permissions...
--WARN-- [boot02] The configuration file /boot/grub/menu.lst has group
permissions. Should be 0600
--FAIL-- [boot02] The configuration file /boot/grub/menu.lst has world
permissions. Should be 0600
--WARN-- [boot06] The Grub bootloader does not have a password configured.
# Checking for vulnerabilities in inittab configuration...
# Checking for correct umask settings for init scripts...
--WARN-- [misc021w] There are no umask entries in /etc/init.d/rcS
# Checking Logins not used on the system ...
# Checking network configuration
--FAIL-- [lin013f] The system is not protected against Syn flooding attacks
--WARN-- [lin017w] The system is not configured to log suspicious (martian)
packets
# Verifying system specific password checks...
# Checking OS release...
--WARN-- [osv004w] Unreleased Debian GNU/Linux version `stretch/sid'
# Checking installed packages vs Debian Security Advisories...
# Checking md5sums of installed files
# Checking installed files against packages...
--WARN-- [lin001w] File `/lib/modules/4.4.0-87-generic/modules.dep' does not
belong to any package.
--WARN-- [lin001w] File `/lib/modules/4.4.0-87-generic/modules.alias.bin' does
not belong to any package.
--WARN-- [lin001w] File `/lib/modules/4.4.0-87-generic/modules.devname' does
not belong to any package.
--WARN-- [lin001w] File `/lib/modules/4.4.0-87-generic/modules.softdep' does
not belong to any package.
--WARN-- [lin001w] File `/lib/modules/4.4.0-87-generic/modules.alias' does not
belong to any package.
--WARN-- [lin001w] File `/lib/modules/4.4.0-87-generic/modules.symbols.bin'
does not belong to any package.
--WARN-- [lin001w] File `/lib/modules/4.4.0-87-generic/modules.builtin.bin'
does not belong to any package.
--WARN-- [lin001w] File `/lib/modules/4.4.0-87-generic/modules.symbols' does
not belong to any package.
--WARN-- [lin001w] File `/lib/modules/4.4.0-87-generic/modules.dep.bin' does
not belong to any package.
--WARN-- [lin001w] File `/lib/modules/4.4.0-89-generic/modules.dep' does not
belong to any package.
--WARN-- [lin001w] File `/lib/modules/4.4.0-89-generic/modules.alias.bin' does
not belong to any package.
--WARN-- [lin001w] File `/lib/modules/4.4.0-89-generic/modules.devname' does
not belong to any package.
--WARN-- [lin001w] File `/lib/modules/4.4.0-89-generic/modules.softdep' does
not belong to any package.
--WARN-- [lin001w] File `/lib/modules/4.4.0-89-generic/modules.alias' does not
belong to any package.
--WARN-- [lin001w] File `/lib/modules/4.4.0-89-generic/modules.symbols.bin'
does not belong to any package.
--WARN-- [lin001w] File `/lib/modules/4.4.0-89-generic/modules.builtin.bin'
does not belong to any package.
--WARN-- [lin001w] File `/lib/modules/4.4.0-89-generic/modules.symbols' does
not belong to any package.
--WARN-- [lin001w] File `/lib/modules/4.4.0-89-generic/modules.dep.bin' does
not belong to any package.
--WARN-- [lin001w] File `/lib/udev/hwdb.bin' does not belong to any package.
# Performing check of root directory...
# Checking device permissions...
--WARN-- [dev003w] The directory /dev/block resides in a device directory.
--WARN-- [dev003w] The directory /dev/char resides in a device directory.
--WARN-- [dev003w] The directory /dev/cpu resides in a device directory.
--FAIL-- [dev002f] /dev/fuse has world permissions
--WARN-- [dev003w] The directory /dev/hugepages resides in a device directory.
--FAIL-- [dev002f] /dev/kmsg has world permissions
--WARN-- [dev003w] The directory /dev/lightnvm resides in a device directory.
--WARN-- [dev003w] The directory /dev/mqueue resides in a device directory.
--FAIL-- [dev002f] /dev/rfkill has world permissions
--WARN-- [dev003w] The directory /dev/vfio resides in a device directory.
# Checking for existence of log files...
--FAIL-- [logf005f] Log file /var/log/btmp permission should be 660
--FAIL-- [logf007f] Log file /var/log/messages does not exist
# Checking for correct umask settings for user login shells...
--WARN-- [misc021w] There is no umask definition for the dash shell
--WARN-- [misc021w] There is no umask definition for the bash shell
# Checking symbolic links...
# Performing check of embedded pathnames...
20:47> Security report completed for username.
More on Tripwire here.
Hardening PHP
Hardening PHP config (and backing the PHP config it up), first create an info.php file in your website root folder with this info
Now look for what PHP file is loading
Back that your PHP config file
TIP: Delete the file with phpinfo() in it as it is a security risk to leave it there.
TIP: Read the OWASP cheat sheet on using PHP securely here and securing php.ini here.
Some common security changes
Don’t forget to review logs, more config changes here.
Antivirus
Yes, it is a good idea to run antivirus in Ubuntu, here is a good list of antivirus software
I am installing ClamAV as it can be installed on the command line and is open source.
ClamAV help here.
Scan a folder
Setup auto-update antivirus definitions
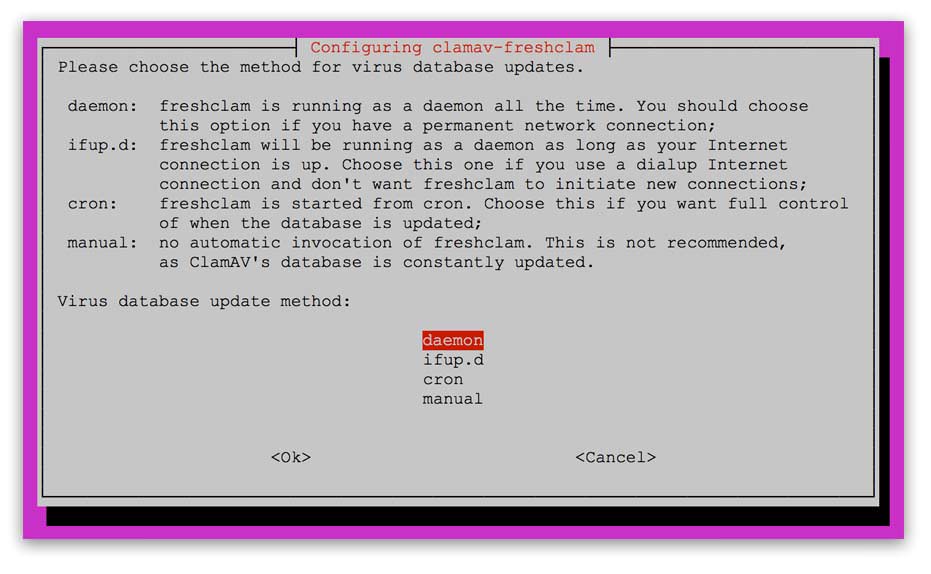
I set auto updates 24 times a day (every hour) via daemon updates.
tip: Download manual antivirus update definitions. If you only have a 512MB server your update may fail and you may want to stop fresh claim/php/nginx and mysql before you update to ensure the antivirus definitions update. You can move this to a con job and set this to update at set times over daemon to ensure updates happen.
Manual scan with a bash script
Create a bash script
Bash script contents to update antivirus definitions.
Edit the crontab to run the script every hour
Uninstalling Clam AV
You may need to uninstall Clamav if you don’t have a lot of memory or find updates are too big.
Setup Unattended Ubuntu Security updates
At login, you should receive
Other
- Read this awesome guide.
- install Fail2Ban
- Do check your log files if you suspect suspicious activity.
Check out the extensive Hardening a Linux Server guide at thecloud.org.uk: https://thecloud.org.uk/wiki/index.php?title=Hardening_a_Linux_Server
Donate and make this blog better
Ask a question or recommend an article
[contact-form-7 id=”30″ title=”Ask a Question”]
v1.92 added hardening a linux server link